Everything you need to know about atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a skin disease and is a very common condition that is seen among many individuals. So how do you really know or diagnose this skin condition? A very typical rash appears on the skin, especially the back of the knee and is distributed over a large patch of skin.
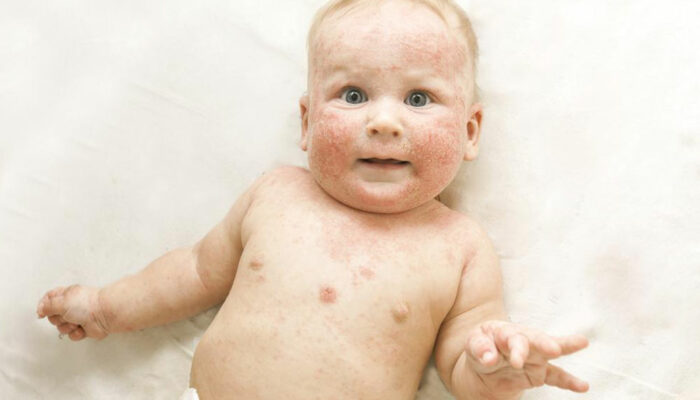
This skin condition causes the affected area to become extremely sensitive, flaky and itchy. It tends to look red and swells up to look cracked and scaled. This condition is a long-term one and may go on for years. While it can improve and clear up completely, there are some periods when the disease can come back and become worse.
The reason or cause behind atopic dermatitis can not be traced down to one factor. There can be several co-effecting elements that can trigger off this condition in an individual. This disease is likely to run down affected families. Kids born from parents with atopic dermatitis are at a higher risk of developing it themselves. It is a type of allergy that is asthma and hay fever. Also, people who have a very skin are more likely to suffer from this disease. The main reason is that the skin is unable to retain moisture and more likely to react to certain elements in the environment.
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis will appear on the exterior part of the skin. Children are most likely to develop the condition on the face and scalp, while an adult will be able to see a patch forming on the hands, elbows or back of the knees. The dry and patchy skin may sometimes look inflamed and may sometimes be less noticeable.
This skin disease can be worsened by several factors such as food allergens, dust, low humidity and low temperatures. It is better to seek medical help has some as the condition triggers or one notices any kind of symptoms. Although this condition can not be entirely cured, it can be controlled through tropical treatment and skin care techniques. Moreover, your gynecologist will perform the certain test and guide you on how you can stop the inflammation from spreading to other parts of the skin.